In the modern world, our diets have undergone a significant transformation, marked by a surge in the consumption of ultra-processed foods. These food products, often laden with additives, preservatives, and refined ingredients, have become ubiquitous on our grocery store shelves. As convenient as they may be, their impact on our health, particularly on blood sugar levels, is a cause for concern.
What Are Ultra-Processed Foods?
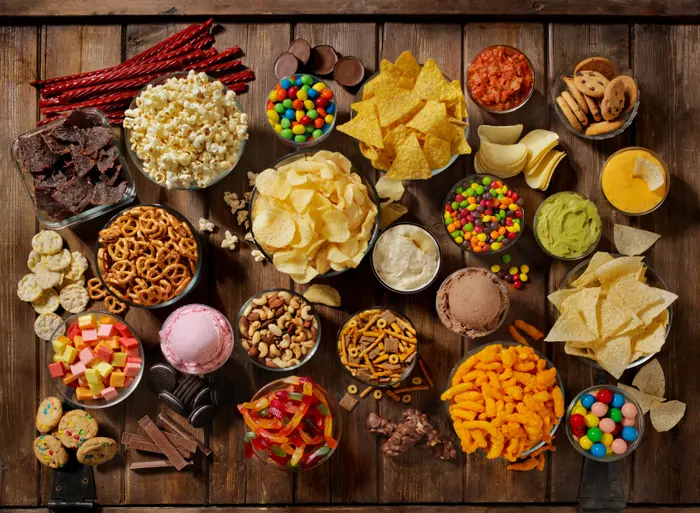

Before delving into their effects on blood sugar, it’s essential to define what ultra-processed foods are. These are products that undergo multiple industrial processes, resulting in a departure from their original form. Examples include sugary cereals, soft drinks, packaged snacks, and ready-to-eat meals. These foods typically contain minimal nutritional value, while their high levels of added sugars, unhealthy fats, and artificial ingredients make them a contributing factor to various health issues.
The Culprits: What Makes Ultra-Processed Foods Harmful?
Ultra-processed foods are often characterized by their high levels of added sugars, unhealthy fats, and artificial additives. These ingredients contribute to the rapid spike in blood sugar levels after consumption, setting off a chain reaction in the body.
The Blood Sugar Rollercoaster: How Ultra-Processed Foods Contribute
Consuming ultra-processed foods can have a pronounced impact on blood sugar levels. These products often have a high glycemic index, causing a rapid spike in blood sugar after consumption. The refined carbohydrates in these foods are swiftly converted into glucose, leading to a surge in blood sugar levels. This rapid increase is often followed by a sharp decline, creating a blood sugar rollercoaster that leaves individuals feeling fatigued, irritable, and craving more sugary snacks to regain energy.
Insulin Resistance and Long-Term Consequences

Repeated exposure to the blood sugar rollercoaster induced by ultra-processed foods can contribute to insulin resistance. Insulin, the hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar, becomes less effective at lowering glucose levels. Over time, this insulin resistance can escalate, leading to prediabetes or type 2 diabetes. The chronic elevation of blood sugar levels is associated with a higher risk of cardiovascular diseases, kidney issues, and other health complications.
Improving Blood Sugar: Making Informed Dietary Choices
To mitigate the impact of ultra-processed foods on blood sugar, adopting a whole-foods-based diet is crucial. Emphasizing nutrient-dense, fiber-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help stabilize blood sugar levels. Limiting the intake of added sugars, refined carbohydrates, and unhealthy fats is equally important. Opting for whole, unprocessed alternatives allows for a more gradual release of glucose into the bloodstream, promoting steady energy levels.
GLP-1 Medications: A Supportive Approach
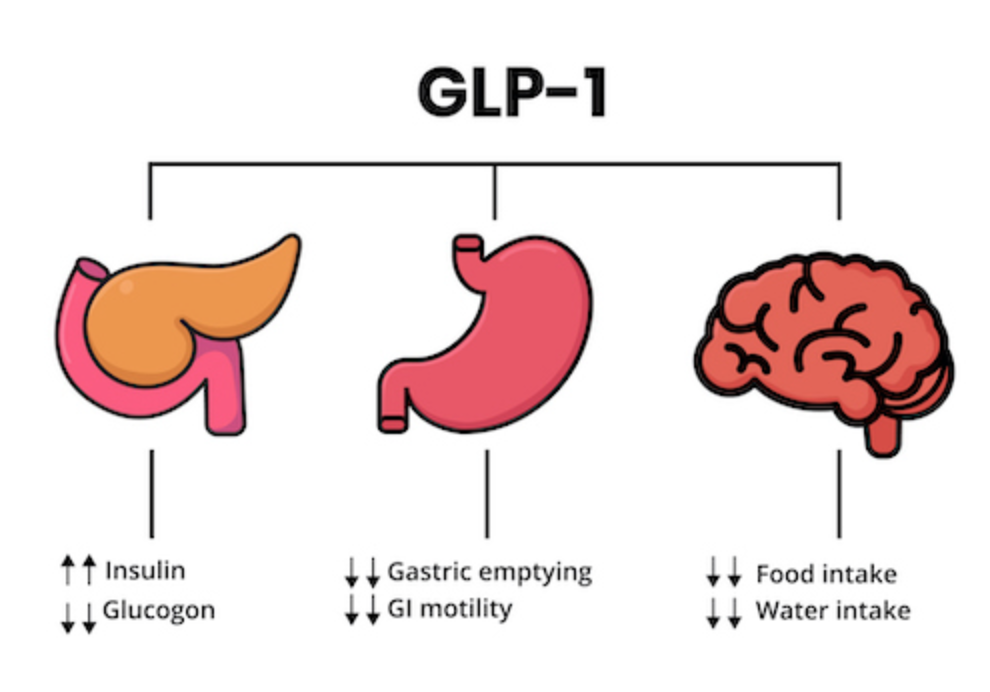
For individuals struggling with blood sugar control, GLP-1 medications offer a valuable adjunct to lifestyle changes. These medications work by mimicking the effects of the hormone GLP-1. They stimulate insulin release, inhibit glucagon, slow digestion, and reduce appetite. This multifaceted approach helps regulate blood sugar levels and can be particularly beneficial for those facing challenges in managing their diet or experiencing difficulty achieving glycemic control through lifestyle changes alone.
Conclusion
The impact of ultra-processed foods on blood sugar is a significant health concern that warrants attention. By making informed dietary choices that prioritize whole, nutritious foods and considering the potential benefits of GLP-1 medications, individuals can take proactive steps toward better blood sugar management and overall well-being. It’s a journey that starts with awareness, education, and a commitment to nurturing our bodies with the wholesome nutrition they deserve.