Obesity is a global health crisis, significantly increasing the risk of various chronic diseases, including cardiovascular disease (CVD). With heart health becoming a primary concern, the link between obesity and...
Obesity is a global health crisis, significantly increasing the risk of various chronic diseases, including cardiovascular disease (CVD). With heart health becoming a primary concern, the link between obesity and CVD is well-established. Fortunately, recent advancements in weight management offer a glimmer of hope.
As a healthcare provider, LifeRx.md is committed to exploring and disseminating groundbreaking treatments that enhance patient outcomes. One such promising therapeutic agent is GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) receptor agonists. Initially approved for type 2 diabetes management, recent studies highlight their potential in weight management and improving heart health in obese individuals.
Understanding the Link Between Obesity and CVD
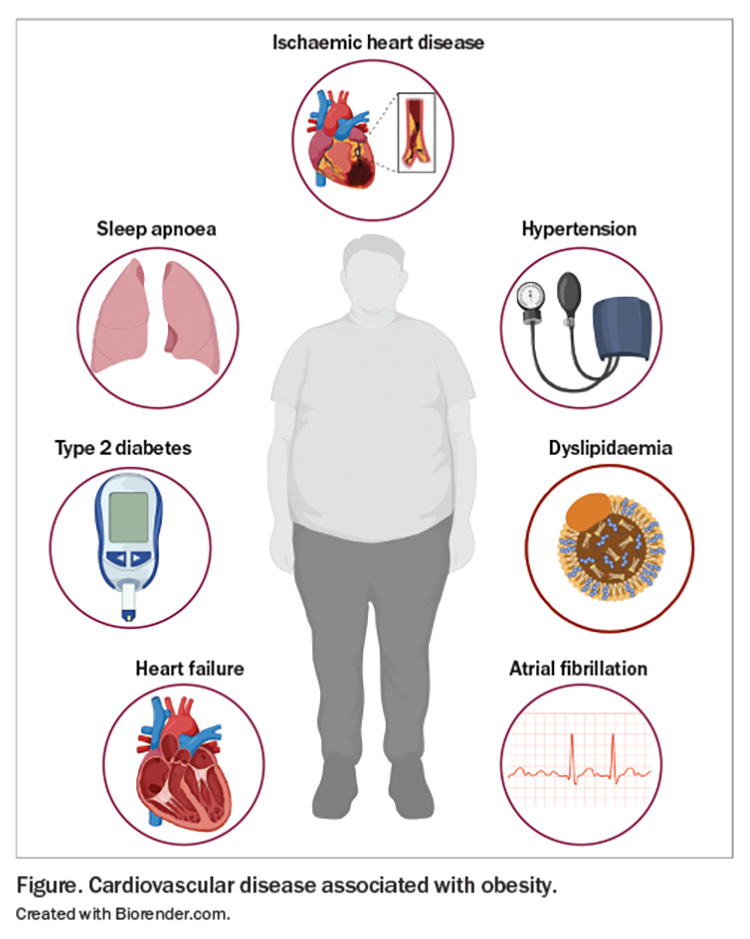
Obesity disrupts the body's metabolic balance, leading to a cascade of detrimental effects. Excess fat accumulation, particularly visceral fat around organs, promotes chronic inflammation, insulin resistance, and dyslipidemia (abnormal blood lipid levels). These factors contribute to the development of atherosclerosis, the hardening and narrowing of arteries due to plaque buildup. Atherosclerotic arteries become less efficient at delivering blood, increasing the risk of heart attack, stroke, and peripheral arterial disease.
GLP-1 and Its Role in Weight Management and Heart Health
GLP-1 is a naturally occurring gut hormone that regulates appetite, blood sugar control, and insulin secretion. GLP-1 receptor agonists mimic these effects, promoting satiety (feeling full), suppressing glucagon (a blood sugar-raising hormone), and enhancing insulin sensitivity. These actions lead to reduced calorie intake, improved blood sugar control, improved heart health and ultimately, weight loss.
Beyond weight management, GLP-1 receptor agonists exhibit additional cardioprotective effects. Emerging research shows that GLP-1:
- Improves Blood Pressure Regulation: GLP-1 promotes vasodilation (relaxation of blood vessels) and reduces inflammation, aiding blood pressure control.
- Modulates Blood Lipids: GLP-1 can lead to favorable changes in blood lipid profiles, potentially lowering LDL ("bad") cholesterol and triglycerides while increasing HDL ("good") cholesterol.
- Reduces Inflammation: By exhibiting anti-inflammatory properties, GLP-1 mitigates cardiovascular risk.
- Enhances Endothelial Function: GLP-1 improves endothelial function, promoting healthy blood flow and reducing the risk of plaque formation.
Clinical Evidence
Several clinical trials and studies underscore the cardiovascular benefits of GLP-1 receptor agonists:
- SUSTAIN-6 Trial: This pivotal trial demonstrated a significant reduction in major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) among patients treated with GLP-1 compared to placebo. The trial reported a 26% reduction in the risk of cardiovascular death, non-fatal myocardial infarction, and non-fatal stroke.
- STEP Trials: These trials focused on the weight management aspect of GLP-1 therapy. The STEP 1 trial, in particular, showed that participants experienced an average weight loss of 14.9% over 68 weeks. This substantial weight reduction correlates with improved cardiovascular outcomes due to decreased obesity-related risk factors.
- PIONEER Trials: These trials evaluated oral GLP-1 therapy, demonstrating similar cardiovascular benefits as its injectable counterpart. These studies provide evidence for the broader applicability and convenience of GLP-1 therapy in different patient populations.
Impact on Specific Cardiovascular Parameters
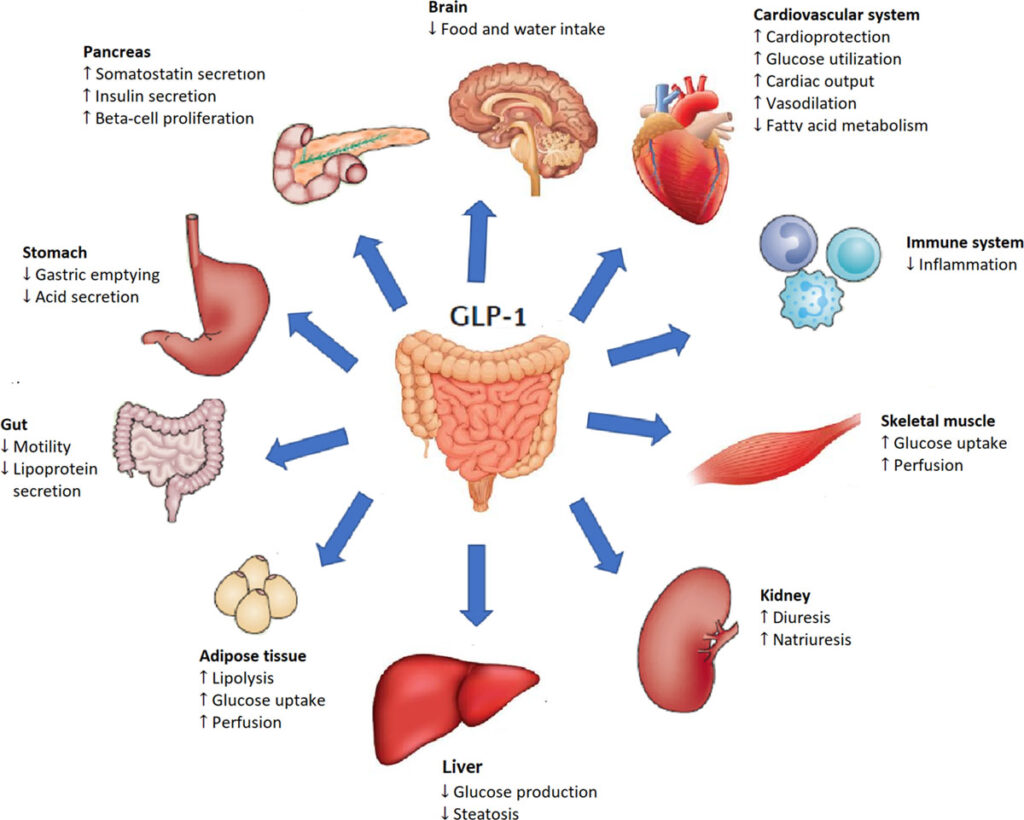
- Blood Pressure: Obesity is often accompanied by hypertension, a major risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. GLP-1-induced weight loss significantly reduces systolic and diastolic blood pressure, attributed to decreased sympathetic nervous system activity and improved endothelial function.
- Endothelial Function: Endothelial dysfunction is a precursor to atherosclerosis. GLP-1 improves endothelial function by enhancing nitric oxide bioavailability and reducing oxidative stress, maintaining vascular health and preventing atherosclerotic changes.
- Left Ventricular Function: Obesity can lead to left ventricular hypertrophy and impaired cardiac function. Studies show that weight loss with GLP-1 therapy results in improved left ventricular function and reduced left ventricular mass, enhancing overall cardiac performance.
- Cardiac Inflammation: High levels of pro-inflammatory markers such as C-reactive protein (CRP) are common in obese individuals and are linked to cardiovascular diseases. GLP-1’s anti-inflammatory effects contribute to lower CRP levels, thus reducing cardiovascular risk.
Comparative Effectiveness
When compared to other weight loss medications and GLP-1 receptor agonists, GLP-1 therapies stand out for their robust cardiovascular benefits. Medications like liraglutide and exenatide offer weight loss and glycemic control benefits, but GLP-1’s superior efficacy in reducing major adverse cardiovascular events makes it a preferred choice for high-risk obese patients.
Safety and Tolerability
The safety profile of GLP-1 receptor agonists is well-established. Gastrointestinal side effects such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea are the most commonly reported but typically improve over time. Importantly, GLP-1 therapies have not been associated with an increased risk of pancreatitis or thyroid cancer in clinical trials.
Practical Considerations for Clinicians
For healthcare providers at LifeRx.md and beyond, incorporating GLP-1 receptor agonists into treatment plans for obese patients requires careful patient selection and monitoring. Ideal candidates are those with a high BMI, comorbid conditions such as type 2 diabetes, and an elevated cardiovascular risk profile. Regular follow-up is essential to monitor weight loss progress, glycemic control, and any potential side effects.
Conclusion
GLP-1 therapies represent a significant advancement in managing obesity and its associated cardiovascular risks. Their multifaceted mechanisms—including weight loss, improved glycemic control, anti-inflammatory effects, and lipid profile enhancement—contribute to substantial cardiovascular benefits. Clinical trials consistently demonstrate their efficacy in reducing major adverse cardiovascular events, making them a valuable addition to the therapeutic arsenal against obesity-related heart disease. At LifeRx.md, we are committed to staying at the forefront of medical innovation, providing our patients with the most effective and evidence-based treatments available.