Maintaining stable blood sugar levels is crucial for overall health, especially for individuals managing conditions like diabetes or those aiming for optimal well-being. One significant challenge many face is controlling blood sugar spikes after meals. Understanding the factors contributing to post-meal glucose fluctuations and implementing effective strategies can significantly impact health outcomes. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the science behind blood sugar spikes, backed by health research, and explore practical tips to keep glucose levels in check.
Understanding Post-Meal Blood Sugar Spikes
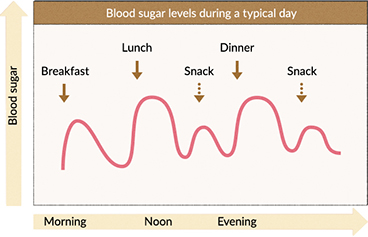
When we consume carbohydrates, our digestive system breaks them down into glucose, causing blood sugar levels to rise. This natural process is amplified after meals, particularly when the meal contains refined carbohydrates or a high glycemic load. Research indicates that postprandial (after-meal) glucose levels play a significant role in overall glucose control, affecting long-term health outcomes .
Choose Low Glycemic Index (GI) Foods
Research consistently highlights the importance of selecting foods with a low glycemic index to mitigate post-meal blood sugar spikes [1]. Foods with a lower GI release glucose more slowly, preventing rapid spikes and promoting sustained energy. Incorporate whole grains, legumes, non-starchy vegetables, and fruits with a lower GI into your meals.
Include Fiber-Rich Foods
Dietary fiber has been shown to have a beneficial impact on postprandial glucose levels [2]. Fiber slows down the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, helping to maintain steadier blood sugar levels. Opt for whole grains, vegetables, fruits, nuts, and seeds to increase your fiber intake and support better glucose control.
Mindful Portion Control
Research emphasizes the importance of portion control in managing post-meal glucose levels [3]. Consuming smaller, well-balanced meals can prevent excessive carbohydrate intake in a single sitting, reducing the potential for glucose spikes. Be mindful of portion sizes, and consider using smaller plates to encourage controlled eating.
Stay Hydrated
Hydration is a simple yet effective strategy to support glucose control. Studies suggest that adequate water intake can influence blood sugar levels, particularly after meals [4]. Aim to stay well-hydrated throughout the day, and consider drinking water with your meals to enhance hydration without adding extra calories or sugar.
Incorporate Physical Activity
Engaging in regular physical activity has been consistently associated with improved blood sugar control. Research indicates that exercise enhances insulin sensitivity, allowing cells to better respond to insulin and regulate glucose uptake [5]. Incorporate both aerobic exercises and resistance training into your routine for comprehensive benefits.
Leverage Vinegar or Apple Cider Vinegar
Emerging research suggests that incorporating vinegar or apple cider vinegar into your diet may help mitigate post-meal glucose spikes [6]. The acetic acid in vinegar appears to slow down the digestion of carbohydrates, resulting in a more gradual release of glucose into the bloodstream. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before adding vinegar to your routine, especially for those with specific health conditions.
Consider Time-Restricted Eating
Time-restricted eating, a form of intermittent fasting, has gained attention for its potential impact on blood sugar control. Research indicates that restricting the time window for food consumption may improve insulin sensitivity and reduce postprandial glucose levels [7]. However, individual responses to this approach may vary, and consultation with a healthcare provider is advisable.
Explore Medication Options
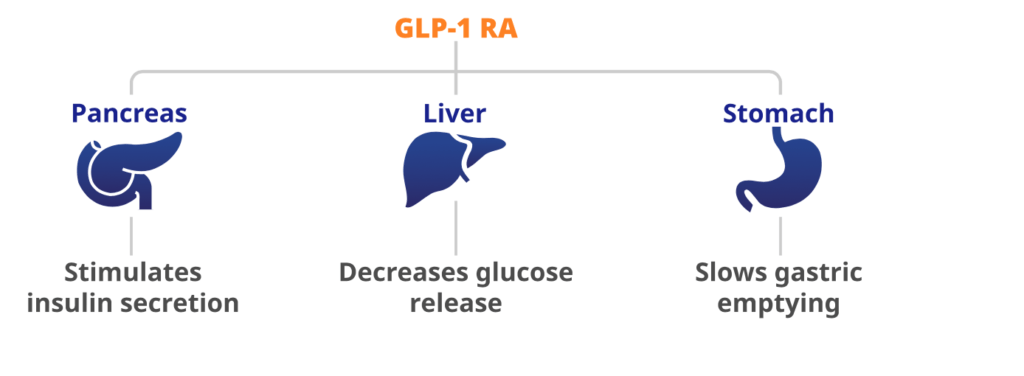
For individuals with diabetes or those at higher risk of post-meal glucose spikes, medications such as GLP-1 agonists may be prescribed. GLP-1 medications work by mimicking the effects of the hormone GLP-1, regulating insulin release and slowing down digestion. These medications can be valuable additions to lifestyle interventions, providing comprehensive blood sugar control [8].
Conclusion: A Holistic Approach to Blood Sugar Control
Effectively managing blood sugar spikes after meals requires a holistic approach that encompasses dietary choices, lifestyle modifications, and, in some cases, medication. By incorporating evidence-based strategies such as choosing low-GI foods, increasing fiber intake, practicing portion control, staying hydrated, engaging in regular physical activity, and exploring emerging options like vinegar or time-restricted eating, individuals can empower themselves to achieve better blood sugar control. As always, consulting with healthcare professionals is essential to tailor these strategies to individual health needs and circumstances.
References:
- The Glycemic Index: Physiological Mechanisms Relating to Obesity, Diabetes, and Cardiovascular Disease
- Dietary Fiber and Blood Glucose Control
- Effects of Portion Size on Weight Loss in Adults
- Effects of Hydration on Plasma Glucose Concentration in Diabetes
- The Role of Exercise in the Treatment of Diabetes
- Effect of Apple Cider Vinegar on Delayed Gastric Emptying in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
- Effects of Intermittent Fasting on Health, Aging, and Disease
- GLP-1 Receptor Agonists for Individualized Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus




