The Inflammation-Weight Gain Connection: What You Need to Know
Chronic, low-grade inflammation – it’s a term we hear thrown around a lot these days, often linked to various health concerns. But did you know there’s a growing body of research suggesting a strong connection between inflammation and weight gain?
At LifeRx.md, we’re dedicated to providing you with the latest science-backed information on achieving optimal health. In this article, we’ll delve deeper into the inflammation-weight gain connection, explore the mechanisms at play, and equip you with valuable insights to manage your weight effectively.
Understanding Inflammation: A Body Under Siege
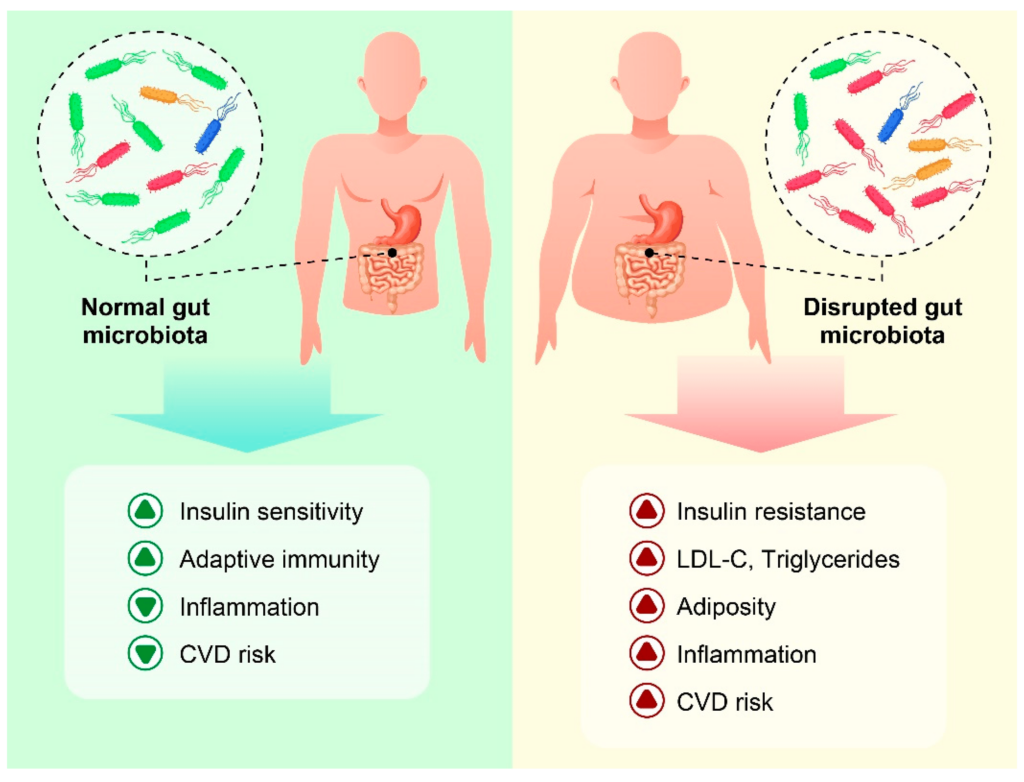
Inflammation is a natural response by the immune system to fight off infections, injuries, and foreign invaders. It’s a complex process involving the release of various immune cells and signaling molecules to isolate and destroy the threat. While acute inflammation is essential for healing, chronic, low-grade inflammation becomes detrimental. It’s like your body being on constant high alert, leading to damage and dysfunction in healthy tissues.
This chronic inflammation can be triggered by various factors, including:
- Diet: Consuming excess sugar, refined carbohydrates, unhealthy fats, and processed foods.
- Stress: Chronic stress activates the sympathetic nervous system, leading to the release of stress hormones like cortisol, which can promote inflammation.
- Lack of sleep: Inadequate sleep disrupts the body’s natural anti-inflammatory processes.
- Gut dysbiosis: An imbalance in gut bacteria.
- Environmental toxins: Exposure to pollutants and chemicals can also contribute to chronic inflammation.
How Inflammation Fuels Weight Gain: A Multifaceted Issue
The link between inflammation and weight gain is complex and multifaceted. Here’s a detailed breakdown of some key mechanisms at play:
- Increased Insulin Resistance
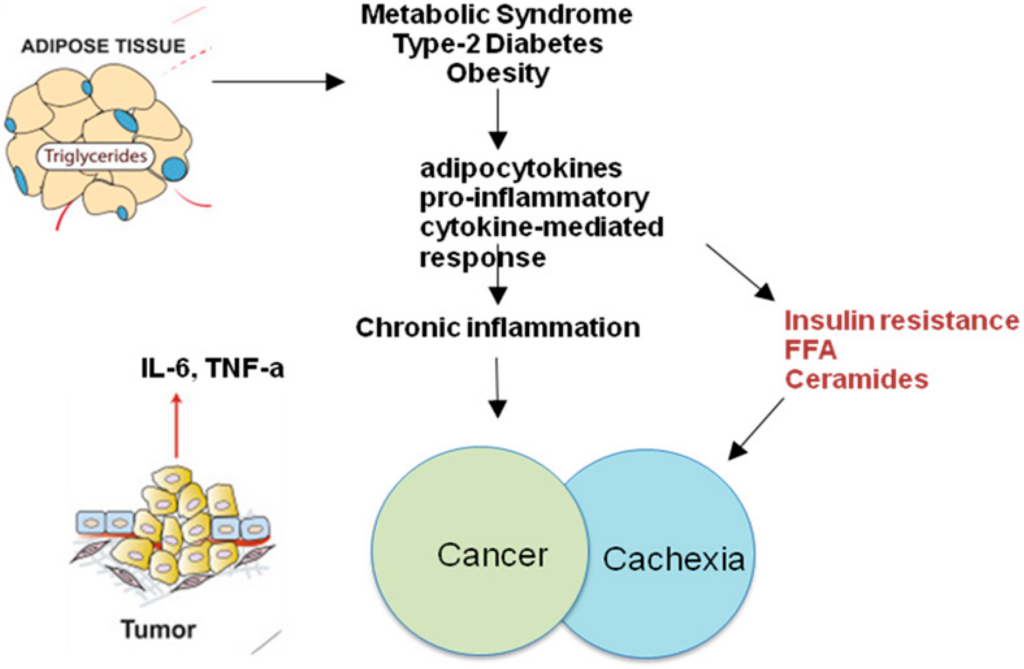
Chronic inflammation disrupts insulin signaling, a hormone crucial for regulating blood sugar. Insulin acts like a key, unlocking cells to allow glucose (sugar) from the bloodstream to enter for energy production. When inflammation is present, these cellular doorways become less responsive to insulin, leading to a condition called insulin resistance. As a result, glucose builds up in the bloodstream instead of being used by cells, leading to high blood sugar levels. The body compensates by producing more insulin to overcome resistance, but over time, this can lead to insulin depletion and difficulty controlling blood sugar. To maintain energy demands, the body turns to fat storage, promoting weight gain.
- Dysregulation of Appetite Hormones
Inflammation can also alter the production of hormones that regulate appetite. Leptin, a hormone produced by fat cells, signals satiety (feeling full) to the brain. Adiponectin, another hormone secreted by fat tissue, also plays a role in regulating appetite and metabolism. Conversely, ghrelin, produced by the stomach, is known as the “hunger hormone” as it stimulates appetite. Chronic inflammation can disrupt the production and secretion of these hormones, leading to increased hunger pangs, decreased feelings of fullness, and difficulty controlling calorie intake, ultimately contributing to weight gain.
- Metabolic Disruption
Inflammation can impair the body’s ability to burn calories efficiently, a process known as metabolism. This can happen through several mechanisms. Inflammatory signaling molecules can interfere with the breakdown of fats and carbohydrates for energy, leading to increased storage. Additionally, chronic inflammation can disrupt mitochondrial function. Mitochondria are the powerhouses of cells, responsible for burning fuel to produce energy (ATP). When inflammation is present, mitochondrial function can become impaired, leading to decreased calorie burning and promoting weight gain.
- Cellular Stress and Damage
Chronic inflammation creates a state of cellular stress throughout the body. This stress can damage and impair the function of various tissues, including muscle. Muscle tissue plays a critical role in metabolism, as it burns calories at rest. When muscle function is compromised the body’s overall metabolic rate can decline, further contributing to weight gain.
Science Sheds Light: Inflammation’s Role in Weight Gain
Different research studies have been conducted that explore the connection between inflammation and weight gain. By including findings from credible sources, we strengthen the credibility of the content and provide readers with a deeper understanding of the scientific evidence.
- A 2018 study published in the journal Nature Medicine investigated the role of a specific molecule, IKK-beta, in the inflammatory process. The researchers found that blocking IKK-beta in obese mice led to significant weight loss and improved insulin sensitivity. This suggests that targeting this specific inflammatory pathway could be a potential therapeutic strategy for obesity and related metabolic disorders.
- A 2014 review published in Current Obesity Reports examined the role of inflammation in obesity and its complications. The review analyzed numerous studies and concluded that chronic, low-grade inflammation is a hallmark of obesity and may play a causative role in its development. The review also highlighted the association between inflammation and obesity-related complications such as insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease.
The Broader Impact of Inflammation
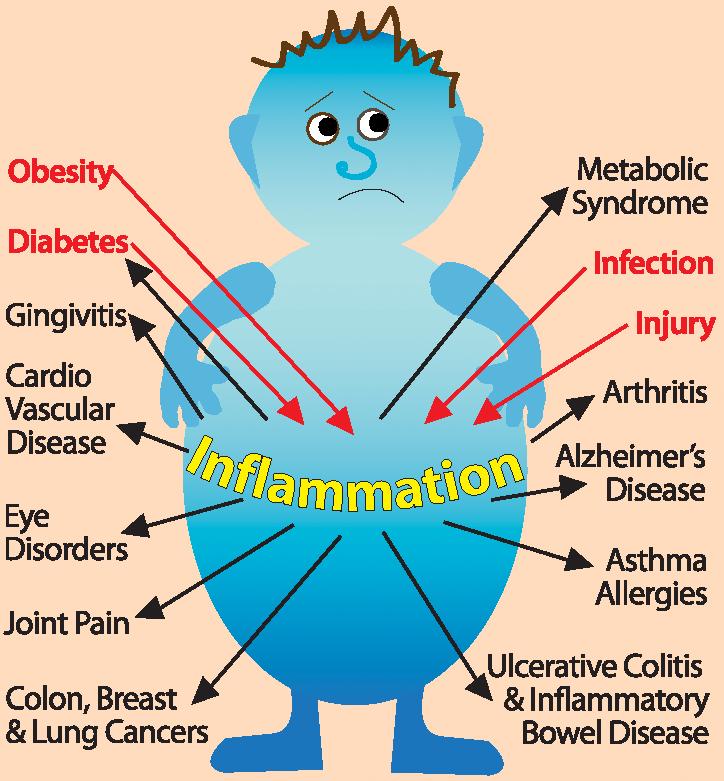
It’s important to remember that weight gain is just one piece of the puzzle. Chronic inflammation is linked to various health concerns, including:
- Heart disease: Inflammation can damage blood vessels and contribute to atherosclerosis, the buildup of plaque in arteries.
- Type 2 diabetes: Chronic inflammation disrupts insulin signaling, a key factor in type 2 diabetes development.
- Certain cancers: Inflammation can promote the growth and spread of cancer cells.
- Autoimmune diseases: Chronic inflammation is a hallmark of many autoimmune diseases, where the immune system attacks healthy tissues.
By addressing chronic inflammation, you’re not just promoting healthy weight management; you’re also taking a proactive step towards overall well-being and reducing your risk of developing various chronic diseases.
Strategies to Combat Inflammation and Manage Weight
The good news is that you have the power to influence your body’s inflammatory state through lifestyle modifications. Here’s how:
- Embrace an Anti-Inflammatory Diet: Prioritize whole, unprocessed foods rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats. Focus on incorporating foods rich in antioxidants like berries, leafy greens, and fatty fish. Consider incorporating spices like turmeric and ginger, known for their anti-inflammatory properties [3, 4]. You can find a wealth of anti-inflammatory recipes on LifeRx.md to guide you on your culinary journey towards better health.
- Manage Stress: Practice stress management techniques like yoga, meditation, deep breathing exercises, or spending time in nature.
- Prioritize Sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Move Your Body: Regular physical activity is a powerful anti-inflammatory tool. Exercise helps to reduce inflammatory markers in the bloodstream and improve insulin sensitivity. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week. Strength training is also crucial, as muscle tissue plays a vital role in metabolism and helps to burn calories at rest.
- Nurture Your Gut: The gut microbiome, the trillions of bacteria residing in your gut, plays a significant role in inflammation. Consume prebiotic-rich foods like yogurt, kefir, and kimchi, which provide nourishment for beneficial gut bacteria. Consider including probiotic supplements after consulting with your healthcare professional.
- Limit Inflammatory Foods: While incorporating anti-inflammatory foods is crucial, it’s equally important to limit those that promote inflammation. This includes refined carbohydrates, sugary drinks, unhealthy fats (trans fats and saturated fats from processed sources), and processed foods.
- Consider Supplements: Certain supplements may be beneficial in reducing inflammation. Consult with your doctor to discuss options like fish oil, curcumin (from turmeric), and resveratrol.
Remember, consistency is key. By incorporating these strategies into your daily routine, you can create a powerful anti-inflammatory lifestyle that supports weight management and overall well-being.
LifeRx.md: Your Partner on the Path to Optimal Health
At LifeRx.md, we understand the complexities of weight management and the critical role of inflammation. We provide a wealth of informative articles, delicious anti-inflammatory recipes, and guidance on various lifestyle modifications to empower you on your journey towards optimal health. We believe in a holistic approach that addresses the root causes of weight gain, promoting lasting, sustainable results.
Visit LifeRx.md today and explore our comprehensive resources to create a personalized plan to combat inflammation, manage your weight effectively, and achieve your health goals!